rids.verify@gmail.com
+91-9555-581-581 | 9401677773

Road Safety
Introduction
India ranks high when it comes to number of accidents on the road. However, in the recent years, improvement has been seen in this area. With the rapid increase in the number of vehicles on the road, the traffic conditions are under a lot of pressure. Therefore, road safety is one of the most serious public health issues in our country. It has an impact on everyone, whether one drives a vehicle, walks or rides a cycle.
Understanding Road Safety
Road safety refers to the measures which must be adopted by everyone while using roads. These safety methods are meant for reducing the risk of accidents and injuries or causalities on the road. These rules must be followed by all users of roads including pedestrians, cyclists, motorists, and bus and truck drivers. Safety methods also relate to the construction, layout of roads as well as traffic regulation systems. So, we can summarise that road safety involves:
(i) The design of roads and highways;
(ii) Laws pertaining to traffic and vehicles;
(iii) Systems of traffic safety and control;
(iv) Driver education;
(v) School students’ education;
(vi) Mass education;
(vii) Traffic regulation and road safety signs;
(viii) Vehicle design; and
(ix) Motor vehicle safety inspection and maintenance.
Keeping our roads safe is not that difficult a task. Imagine if everyone follows simple safety measures and traffic rules, there will be no accident!
In this Unit, you will understand the various types of road safety measures to be adopted, and the importance of safety rules, road signs, traffic signals and rules, driving rules, registration and licensing adopted in our country.
Session 1: Importance of Road Safety
Road Safety
Some of the major causes of road accidents are as
follows.
(i) Lack of highway safety
(ii) Drunken driving
(iii) Driving in an exhausted state for long hours
(iv) Using cell phone while driving
(v) Over speeding or rash driving
(vi) Driving in wrong lanes
(vii) Turning without giving signal
(viii) Overtaking from wrong side
It can be seen that road safety is a collective responsibility. Therefore each one of us has to take steps required of us.
Role of Government and Public Sector
(i) Develop stricter road safety polices
(ii) Generate funds for road safety awareness
(iii) Stricter enforcement of rules by government
(iv) Building better roads and highways
Role of General Community
(i) Acceptance of road safety rules, regulations and policies
(ii) Participation in road safety awareness drives to enhance people’s knowledge about road safety
Role of Education Sector
(i) Inclusion of road safety modules in school curriculum
(ii) Impart road safety education with the help of experts in this area
(iii) Impart effective driver training for learners as well as existing drivers
Role of Media
(i) Communicate road safety messages through print and electronic media
(ii) Support road safety initiatives through responsible and objective reporting
Role of Health Professionals
(i) Strengthen trauma facilities in our country.
(ii) Organise workshops for saving the lives of people in road accidents
Improvement in Infrastructure
(i) Adopt effective and safe traffic management measures while planning and designing infrastructure. For example, government approved road design, design of overbridges, road signages, etc.
Hurdles in Road Safety
(i) Negligence by civilians
(ii) Pathetic condition of roads
(iii) Unsafe vehicle design
(iv) Violation of road safety standards
(v) Lack of emergency services
(vi) Defects in highway designing
Some measures undertaken by the Road Safety Cell are
(i) Publicity programmes
(ii) Grants-in-aid to voluntary organisations for organising road safety programmes
(iii) National Highway Accident Relief Service Scheme
(iv) Refresher training to heavy vehicle drivers in unorganised sector
(v) Setting up of Model Driving Training school
(vi) Within the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, massive road sector development programmes, such as observing Road Safety Week or conducting eye check-ups for truck drivers, the government is working closely with agencies like the World Bank, Asian Development Bank to improve road safety.
Road Safety Tips
Road safety is a result of efforts from all the sectors of the society including civilians and government officials.
In addition to the human suffering, the estimated cost of road injuries is a noticeable amount in Gross National
Product (GNP) per annum.
A few important road safety tips are mentioned below.
(i) Do not use your mobile phone while driving.
(ii) Use seatbelts even while sitting at the back seat of
the vehicle.
(iii) Do not drink and drive.
(iv) Always adhere to the speed limit.
(v) Take special care with regard to children, senior
citizens and pedestrians.
(vi) Do not drive if tired.
(vii) Pedestrians should walk cautiously and make use
of zebra crossing.
(viii) Stay alert and observant while driving.
(ix) Keep distance from other vehicles while driving.
(x) Always wear helmets and seatbelts.
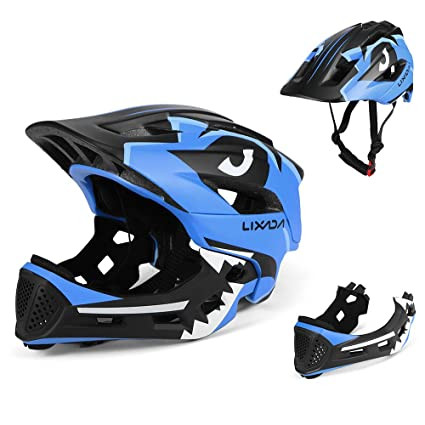

Two-wheeler Helmet
A two-wheeler helmet (Figs 4.2, 4.3) is a type of protective headgear used by bicycle, motorcycle and scooter riders. The primary goal- of a two-wheeler helmet is to protect the rider’s head during impact, thus preventing or reducing head injury or saving the rider’s life. Some helmets provide additional conveniences, such as ventilation, face shields, ear protection, etc.
Of all the organs in our body, the heart and brain are the most vital ones. When a two-wheeler rider meets with an accident, it is the brain that is at a greater risk of injury. A brain injury can result due to skull fracture,
a concussion, brain haemorrhage, which can result in death.
Even if a part of the brain is damaged, it might result in the loss of speech or motor skills. In order to protect the brain, one must wear a helmet. A motorcycle helmet protects the skull and the brain from extensive damage.
Session 2: Safe and Responsible Driving
Getting Ready to Drive before Driving
(i) Ensure that you are comfortable with your mental and physical condition.
(ii) Inspect your vehicle and observe the driving conditions.
While driving, you should carry your driving licence, registration certificate, insurance certificate and pollution control certificate. Transport and commercial vehicle drivers should carry the permits and vehicle fitness certificates also.
A combination of knowledge, skill and attitude is required to be a safe driver.
Knowledge of traffic rules and driving practices that help traffic move safely.
Skill to care about the safety of others on the road. We all are responsible for avoiding accidents.
Attitude to cooperate with other drivers to keep traffic moving safely. We must be courteous, giving other drivers space to change lanes, not cutting them off and signalling before turning.
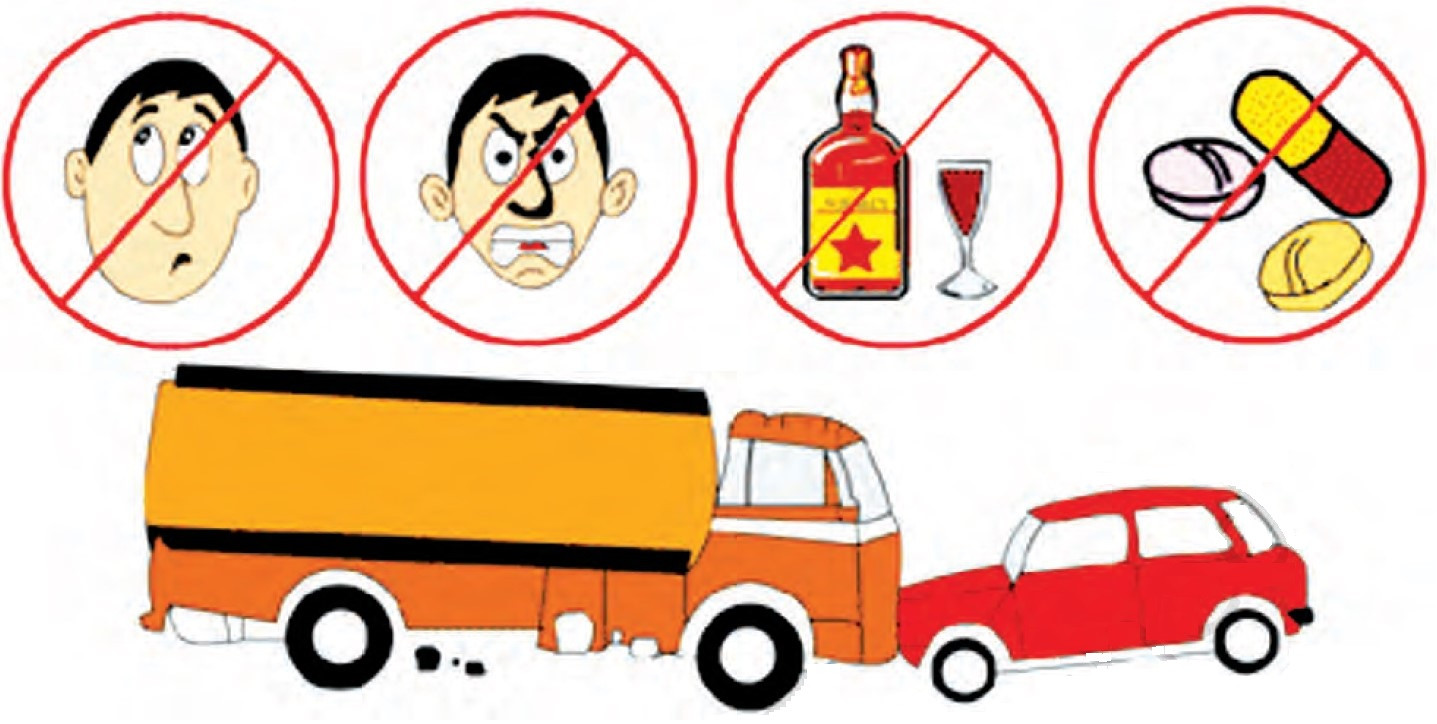

Physical and Mental Alertness
One must be in good physical and mental condition before driving (Fig. 4.5).
Do not drive if you
(i) have been drinking alcohol.
(ii) take any medicine or drug that affects your responses.
(iii) are tired, as it affects your driving skills and reaction time.
(iv) are sick or injured.
(v) are angry or upset.
In such conditions, you could be risking your life or lives of others on the road.
Know Your Vehicle
Go through the vehicle owner’s manual.
You should know the features of the vehicle you are going to drive, for example, anti-lock brakes, four‑wheel drive, etc.
Ensure that you know where the controls and instruments are and what they do. Check that all emergency signals and instruments work.
You should be able to turn on wipers, washers, headlights, indicators, etc., without having to look at them and without taking your eyes off the road.
Seating Position
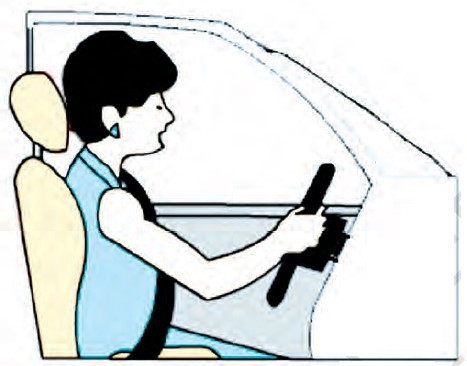
Proper, upright position gives more stability while driving. Make sure you can see over the steering wheel and hood. You should be able to see the ground 1.5–2.0 metre in front of the vehicle for proper judgement.
Sit straight and upright in the seat, with your elbows slightly bent. Adjust the seat (Fig. 4.6) so that your feet reach the pedals easily. Place your feet flat on the floor under the brake pedal. You are seated properly if you can do this.
Adjust the headrest to an appropriate height. It protects the head in case of collision.
Cars with air bags: It is important to note that an air bag cannot prevent injuries if the seating position is incorrect
Know Your Blind Spots
Blind spot (Fg. 4.7) is an area on each side of the vehicle that you cannot see through the mirrors. Mostly blind spots are to the back
left and back right of the vehicle. In Fig. 4.7, the red car is in the blind spot area of the silver car. The green areas show the blind spots
of the silver car.
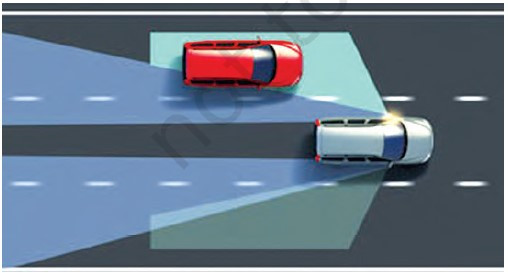
Adjust the mirrors to get the maximum view and identify your blind spots. You may not see vehicles when they are in these spots.
Position the interior mirror so that the centre of the mirror shows the centre of the rear window. When the interior mirror is properly adjusted, you would be able to see directly behind your vehicle
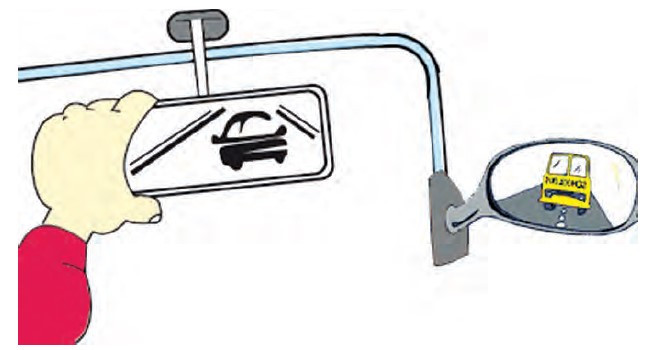
The exterior (wing) mirror adjustment should be made while seated normally for driving. Do not set the right-hand exterior mirror by placing your head against the glass of the driver’s door window. Do not adjust the left-hand exterior mirror by leaning to the centre of the vehicle.
Side mirrors show only narrow angles of view, so you have to turn your head to make sure there is nothing in your blind spots.
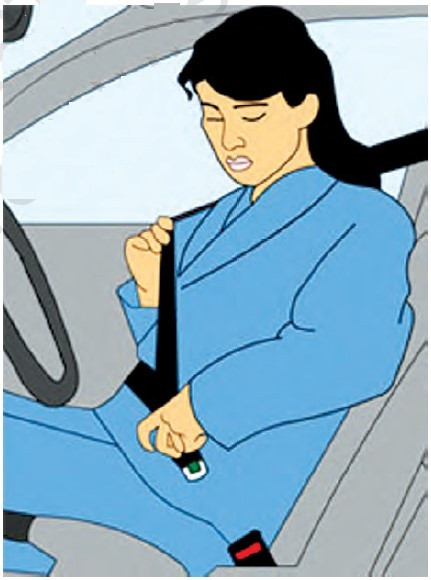
Fasten your Seat Belt
Fasten your seat belt before you start Seat belts are for safety and not just for avoiding challans.
Seat belts should be worn comfortable enough to keep you in your seat if there is a collision. Put the shoulder strap over your shoulder, never under your arm. The lap belt should be put low over the hips, not over the stomach.

A seat belt saves life in the following ways.
(i) It keeps you behind the wheel and in control of the vehicle in case of a collision.
(ii) It keeps your head and body from hitting the inside of the vehicle.
(iii) It keeps you inside the vehicle in case of a collision. A person who is thrown out of the vehicle during the collision has a higher chance of serious injury.
Session 3: Road Signs
Signals play an important role during smooth movement of traffic. Road signals are to be followed systematically, otherwise it may cause accidents.
Arm Signals
Arm signals are needed when a vehicle’s indicators are not used, or when necessary to reinforce direction indicator signals and stop lights







